
A solar cell is a photoelectric cell that converts light energy into electrical energy. Specifically known as a photovoltaic or PV cell, the solar cell is also considered a p-n junction diode.
It has specific electrical characteristics, such as current, resistance, and voltage, that change under light exposure.
Users can combine individual solar cells to create modules commonly known as solar panels. The single-junction solar cell made of silicon can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage. This voltage is approximately 0.5 to 0.6 volts.
A Solar cell is small, and when combined with a large solar panel, large amounts of renewable energy are generated. A solar cell is made up of boules of silicon.
What Are Solar Cells?
A solar cell, referred to as a photovoltaic cell is used to convert light energy into electricity. The effect it uses is the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
Did you know that individual solar cell devices are the main parts of photovoltaic modules? They are also called solar panels in the local language.
Solar cells are photovoltaic, whether the energy source is sunlight or artificial light. They are useful in producing energy and electromagnetic radiation, and measuring light intensity.
The operation of PV cells needs three main things-
- Excitons, absorption of light, and plasmons or unbound electron-hole pairs.
- Charge carrier separation.
- Extraction of carriers to an external circuit.
Construction of Solar Cells – How Is A Solar Cell Made?
A solar cell is a junction diode. The construction of a solar cell varies from that of a standard p-n junction diode. First, a thin layer of p-type semiconductor is allowed to contact a thick n-type semiconductor. Then, on the p-type semiconductor, a few finer electrodes are applied.
These fine electrodes do not cause any obstruction in the pathway of the light to reach the thin p-n junction. A current collecting electrode is also placed at the bottom of the n-type layer.
In addition, manufacturers can also encapsulate the assembly using thin glass to help prevent mechanical shocks in the solar cell. The encapsulated solar cells can be placed in an aluminium frame with a Tedlar back sheet.
How do solar cells function: The working principle behind solar cells
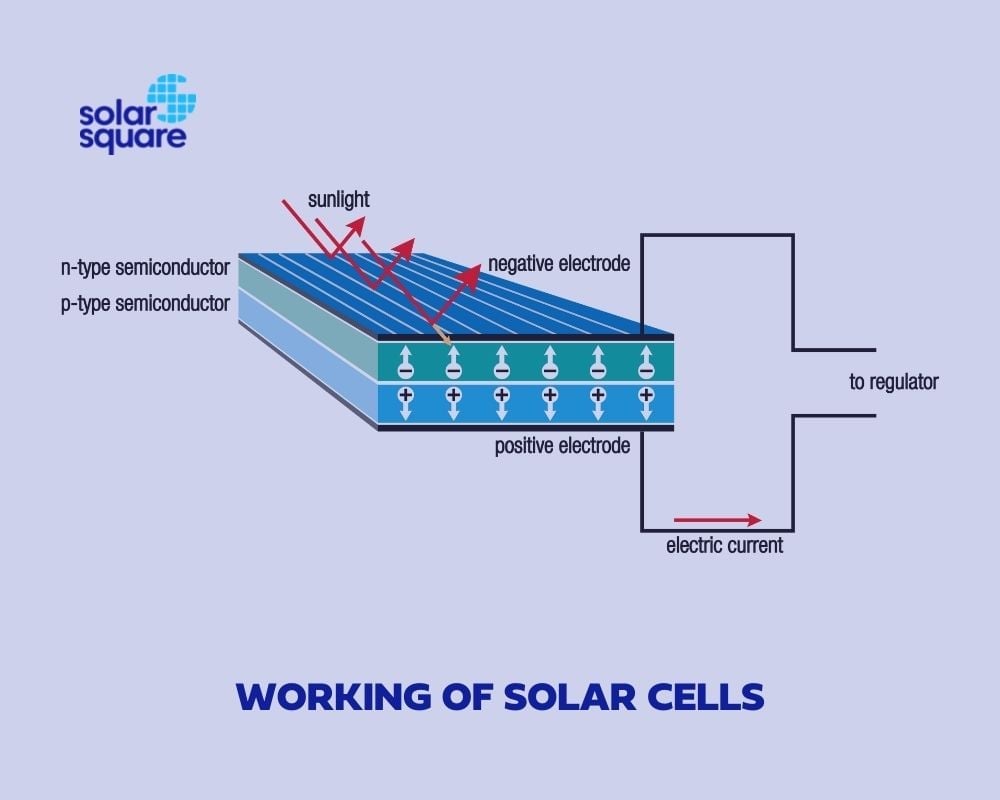
When light reaches the p-n junction between the p and n-type semiconductors, photons easily enter through a thin p-type layer.
The photons provide energy to the p-n junction, creating electron-hole pairs. This light disrupts the thermal equilibrium condition of the junction, encouraging the free electrons to move to the n-type side of the junction.
The holes move to the junction’s p-type side in a similar pattern. As a result, free electrons on the n-type side fail to move past the junction due to a potential barrier.
The same barrier potential of the junction blocks the newly-created holes, causing an increased concentration of electrons on one side (at the n-type junction) and holes on the other side. This process allows the p-n junction to operate as a battery cell.
Types of solar cells:
- Amorphous Silicon solar cell (a-Si)
- Dye-sensitised solar cell (DSSC)
- Hybrid solar cell
- Biohybrid solar cell
- Cadmium telluride solar cell (CdTe)
- Float-zone silicon
- Photoelectrochemical cell (PEC)
- Quantum dot solar cell
- Monocrystalline solar cell (mono-Si)
- Multi-junction solar cell (MJ)
- Organic solar cell (OPV)
- Gallium arsenide germanium solar cell (GaAs)
- Perovskite solar cell
- Non-concentrated heterogeneous PV cell
Power generation from a solar cell
Solar cells have two silicon layers – the p-type and n-type layers. The n-type semiconductor can give away electrons while facing the light. Meanwhile, the p-type conductor receives extra electrons in the extra holes.
This p-type semiconductor is placed beneath the n-type conductor. The solar energy from the sun in the form of photons creates loose electrons on the n-type semiconductor and holes on the p-type semiconductor. These loose electrons get collected on the aluminium layer and start flowing; thus, forming an electric current.
Solar Cell Price
Solar panel price in India is approximately Rs. 45,000 to Rs. 50,000. However, the solar cell price range varies from about 10-20%, depending on the brand and location.
Furthermore, there are other factors like government subsidies and the type of solar panel. As per eligibility, the state or central government allows up to 40% subsidy. A few states even have subsidies up to 70%.
Pros and Cons of Solar cells
Pros of solar cells-
- Conservation of energy
- Non-polluting
- Long-lasting use
- Zero maintenance costs
Cons of solar cells-
- High installation costs
- Low efficiency as compared to electricity
- Doesn’t work on a cloudy day
Why isn’t solar energy more popular?
Solar energy helps us reduce our carbon footprints. Well, then what stops it from becoming popular?
- Cost of installation – Manufacturing, installation, and recycling costs are big inhibitors to solar energy gaining more ground in India. Furthermore, due to the maintenance costs, solar energy is a less popular choice for the domestic power supply.
- Lack of Space – Solar panels need a huge area to be installed. This proves to be a problem in residential areas.
That, however, doesn’t mean that solar power isn’t the future. Solar energy is underrated.
With the kind of subsidy schemes that the govt offers and the EMI financing options that solar panel installers propose, the cons can be easily overpowered.
Conclusion
With technological advancements, the cons or disadvantages associated with solar energy are diminishing, leading to increased participation from the public.
In addition, these advancements will bring down the costs of installation and manufacturing, allowing everyone to contribute towards saving energy and reducing their carbon footprints.
FAQs
1. What are the main uses of Solar Generation Systems?
The top three uses of solar generation systems are-
- Useful for charging batteries.
- Useful for charging calculators and watches.
- Useful in light meters.
2. Will my solar panel produce energy even when it is cloudy?
A solar panel generates energy from the sun. Therefore, a solar panel will produce energy only if the sun shines. Due to this, if the day is cloudy, your solar panel will produce less electricity on that day.
3. Are solar panels suitable for domestic use?
Solar panels are made of materials sufficiently resistant to external weather. Therefore, they are suitable for domestic as well as industrial usage.
